Artificial Intelligence Training by Experts
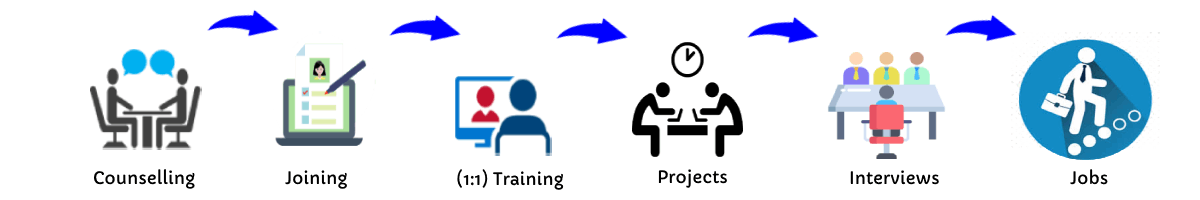
Our Training Process
Artificial Intelligence - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
Module 1: Introduction to Data Science
- What is Data Science?
- What is Machine Learning?
- What is Deep Learning?
- What is AI?
- Data Analytics & it’s types
Module 2: Introduction to Python
- What is Python?
- Why Python?
- Installing Python
- Python IDEs
Module 3: Python Basics
- Python Basic Data types
- Lists
- Slicing
- IF statements
- Loops
- Dictionaries
- Tuples
- Functions
- Array
- Selection by position & Labels
Module 4: Python Packages
- Pandas
- Numpy
- Sci-kit Learn
- Mat-plot library
Module 5: Importing Data
- Reading CSV files
- Saving in Python data
- Loading Python data objects
- Writing data to csv file
Module 6: Manipulating Data
- Selecting rows/observations
- Rounding Number
- Selecting columns/fields
- Merging data
- Data aggregation
- Data munging techniques
Module 7: Statistics Basics
- Central Tendency
- Probability Basics
- Standard Deviation
- Bias variance Trade off
- Distance metrics
- Outlier analysis
- Missing Value treatment
- Correlation
Module 8: Error Metrics
- Classification
- Regression
Module 9: Machine Learning
- Supervised Learning
- Linear Regression
- Logistic regression
Module 10: Unsupervised Learning
- K-Means
- K-Means ++
- Hierarchical Clustering
Module 11: SVM
- Support Vectors
- Hyperplanes
- 2-D Case
- Linear Hyperplane
Module 12: SVM Kernel
- Linear
- Radial
- polynomial
Module 13: Other Machine Learning algorithms
- K Nearest Neighbour
- Naïve Bayes Classifier
- Decision Tree CART
- Decision Tree C50
- Random Forest
Module 14: ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
- Perceptron
- Multi-Layer perceptron
- Markov Decision Process
- Logical Agent & First Order Logic
- AL Applications
Module 15: Deep Learning Algorithms
- CNN Convolutional Neural Network
- RNN Recurrent Neural Network
- ANN Artificial Neural Network
Module 16: Introduction to NLP
- Text Pre-processing
- Noise Removal
- Lexicon Normalization
- Lemmatization
- Stemming
- Object Standardization
Module 17: Text to Features
- Syntactical Parsing
- Dependency Grammar
- Part of Speech Tagging
- Entity Parsing
- Named Entity Recognition
- Topic Modelling
- N Grams
- TF IDF
- Frequency / Density Features
- Word Embedding
Module 18: Tasks of NLP
- Text Classification
- Text Matching
- Levenshtein Distance
- Phonetic Matching
- Flexible String Matching
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates





 Deep Learning is at the heart of AI, which might be a basic software development capability. Data Analytics is the pre-processing activity of AI. Computers, on the other hand, will avoid making these errors if they are correctly programmed. These errors can have a significant impact, ranging from wasting money to putting a patient's life in jeopardy. Now and again, humans make blunders. Even though AI has been studied for more than half a century, we have yet to produce a machine that is as intelligent as a human. Currently, AI technology is used in a variety of fields, including transportation, finance, medicine, and education. Our online education program requires you to become an Advanced Industrial Technologies specialist. Artificial intelligence is an arena of training that looks into how intelligent human behavior can be replicated on a machine. Firms can use this to simulate various scenarios and change the required activities to increase efficiency.
Deep Learning is at the heart of AI, which might be a basic software development capability. Data Analytics is the pre-processing activity of AI. Computers, on the other hand, will avoid making these errors if they are correctly programmed. These errors can have a significant impact, ranging from wasting money to putting a patient's life in jeopardy. Now and again, humans make blunders. Even though AI has been studied for more than half a century, we have yet to produce a machine that is as intelligent as a human. Currently, AI technology is used in a variety of fields, including transportation, finance, medicine, and education. Our online education program requires you to become an Advanced Industrial Technologies specialist. Artificial intelligence is an arena of training that looks into how intelligent human behavior can be replicated on a machine. Firms can use this to simulate various scenarios and change the required activities to increase efficiency.