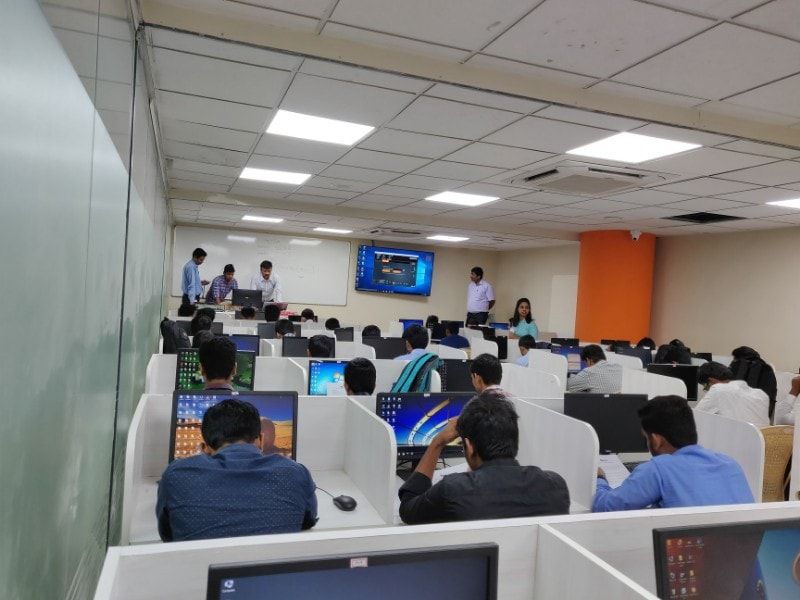
Java J2EE Training by Experts
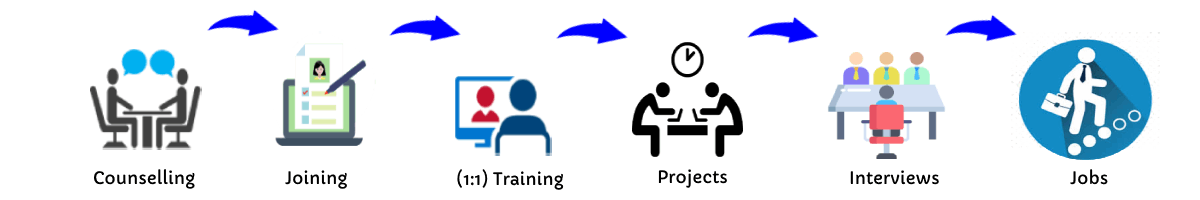
Our Training Process
Java J2EE - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
Module 1: Basics of Java
- Introduction
- History
- Features of Java
- Types of Java Application
- Difference between JVM,JRE and JDK
- Simple Java Program
- Variables and Data types
- Methods-Declaration, definition and Calling
- Packages
- Access modifiers
- Reading from Console using Scanner
- Java Arrays
- Operators and Operator precedence
- Conditional and Looping Statements
- Basic Java Programs
Module 2: String Handling in Java
- String class Introduction
- Immutable String
- Methods of String Class
- String Comparison
- String Concatenation
- String Buffer Class
- String Builder Class
- Mutable String
- toString method
Module 3: Wrapper Classes
- Wrapper classes
- Autoboxing
- Unboxing
Module 4: OOPS Concepts
- OOPs Concepts Introduction
- Object and class
- Static keyword
- Constructor
- this keyword
- Inheritance
- Aggregation and Composition
- super Keyword
- Interface
- Polymorphism
Module 5: Exception Handling
- Exception Handling Introduction
- try and catch block
- Multiple catch block
- Nested try
- finally block
- throw keyword
- throws keyword
- Exception Handling with Method Overriding
- Custom Exception
Module 6: Multithreading
- Multi threading Introduction
- Multi threading vs Multiprocessing
- Life Cycle of a Thread
- Creating a Thread
- Thread Class
- Runnable Interface
- Thread class methods
- Thread Scheduler
- Thread Priority
- Daemon Thread
- Thread Pooling
- Thread Group
- Performing multiple task by multiple thread
Module 7: Synchronization
- What is Synchronization and Why?
- Synchronized method
- Synchronized block
- Static synchronization
- Deadlock
Module 8: Garbage Collection
- What is garbage collection?
- finalize method
Module 9: AWT and Event Handling
- AWT Controls
- Event Handling by 3 ways
- Event classes and Listener Interfaces
- Adapter classes
Module 10: Layout Managers
- Basics of Swing
- Swing features
- Advantages of swing over AWT
- Swing Components
- Digital Watch
- Graphics in swing
- Displaying Image
- Open Dialog Box
- Drawing paintings
- Creating applications
Module 11: Applet
- Applet features
- Life Cycle of Applet
- Graphics in Applet
- Displaying image in Applet
- Animation in Applet
- Event Handling in Applet
- J Applet class
- Painting in Applet
- Creating Animations
Module 12: Collection
- Collection Framework
- Array List class
- Linked List class
- List Iterator interface
- Hash Set class
- Linked Hash Set class
- Tree Set class
- Priority Queue class
- Map interface
- Hash Map class
- Linked Hash Map class
- Tree Map class
- Hash table class
Module 13: Java Updated Features
- Functional Interface and Lambda Expression
- Java Stream API for Bulk Data Operations on Collections
- Java Time API
Module 14: SQL
- Introduction
- Basic SQL Queries
- DDL,DML and DCL
- Aggregation in SQL
- Joining tables
- Subqueries
Module 15: JDBC
- JDBC Drivers
- Steps to connect to the database
- Connectivity with Oracle, MySQL and Access
- Driver Manager
- Connection interface
- Statement interface
- Result Set interface
- Prepared Statement
- JDBC New Features
- Mini Project using swing and JDBC
Module 16: Web Technology
HTML 5
- Introduction to HTML
- HTML Tags
- Lists
- Forms creation
- Creating tables
- Managing home page
CSS
- Introduction to CSS
- Three ways to use CSS
- CSS selectors
- CSS Properties
- Designing website
JavaScript
- Introduction to JavaScript
- Syntax
- Three ways to use JavaScript
- Variables
- Data types
- Operators
- Conditional and Looping Statements
- Functions
- Working with events
- Client-side Validation
jQuery
- Introduction to jQuery
- jQuery syntax
- Example program
- jQuery selectors
- jQuery Effects
- jQuery Events
- Validation using jQuery
- jQuery Forms
- jQuery Examples
AJAX
- Introduction to AJAX
- Servlet and JSP with AJAX
- Interacting with database
Module 17: Server Side Programming
- Servlet
- Servlet introduction
- Basics of Web
- Servlet vs CGI
- Servlet API
- Servlet Interface
- Generic Servlet
- Http Servlet
- Servlet Life Cycle
- How servlet works?
- Servlet Request
- Servlet Request methods
- Registration example with DB
- Request Dispatcher
- send Redirect
- Servlet Config
- Servlet Config methods
- Attribute
- Session Tracking
- URL Rewriting
- HTTP Session
- JSP
- Basics of JSP
- Life cycle of JSP
- JSP API
- Scripting elements
- scriptlet tag
- expression tag
- declaration tag
- 9 Implicit Objects
- Directive Elements
- Exception Handling
- Action Elements
- Expression Language
- MVC in JSP
- JSTL
- Custom tags
- Interacting with database
- Project Development in JSP
Module 18: Hibernate
- Hibernate Configuration using XML and annotation.
- Hibernate CRUD operation
- Hibernate Query Language
- Mapping One to One
- One to many
- Many to one
- Many to Many
- Fetching types
Module 19: Spring Framework
- Basics of Spring
- Spring with ORM
- Spring 3 MVC
- Login and Logout Application
- CRUD Functions
- Main Project
- Spring Boot
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 The course content of our best J2EE online training in Montreal has been carefully tailored to meet the needs of the industry. It enables programmers to create applications that work on both single-processor computers and multi-processor systems.
.
If you decide to pursue java as a career, you will have a plethora of options. As a result, Java is one of the most popular programming platforms for developing enterprise applications. As a result, the primary focus of this course is on learning JAVA-based technologies. Our Java training classes are organised in a way that makes learning easy and enjoyable. Many well-known companies, like Facebook, Netflix, Spotify, Amazon, and others, use Java to develop their products. The Java EE platform's goal is to provide developers with a strong set of APIs while lowering development time, increasing application complexity, and improving application performance. J2EE Course on {Location} comprises subjects that cover the most recent and greatest examples in real-time, all of which are meant to assist learners in landing the right job after completing the course.
The course content of our best J2EE online training in Montreal has been carefully tailored to meet the needs of the industry. It enables programmers to create applications that work on both single-processor computers and multi-processor systems.
.
If you decide to pursue java as a career, you will have a plethora of options. As a result, Java is one of the most popular programming platforms for developing enterprise applications. As a result, the primary focus of this course is on learning JAVA-based technologies. Our Java training classes are organised in a way that makes learning easy and enjoyable. Many well-known companies, like Facebook, Netflix, Spotify, Amazon, and others, use Java to develop their products. The Java EE platform's goal is to provide developers with a strong set of APIs while lowering development time, increasing application complexity, and improving application performance. J2EE Course on {Location} comprises subjects that cover the most recent and greatest examples in real-time, all of which are meant to assist learners in landing the right job after completing the course.