MongoDB Training by Experts
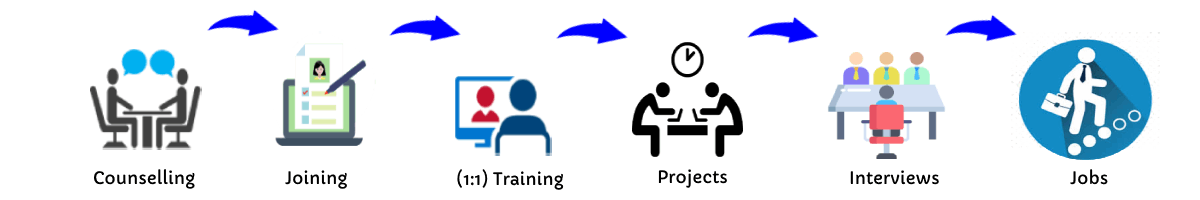
Our Training Process
MongoDB - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
Module 1: Introduction to NoSQL
- What Is NoSQL?
- Why NoSQL databases are required
- Types of NoSQL Database
- NoSQL vs SQL Comparison
- ACID & BASE Property
- CAP Theorem
- Benefits of NoSQL databases
- Installation
- Start and Stop the MongoDB process
Module 2: MongoDB Architecture
- Document, Collection, Databases
- JSON and BSON
- Storage Engines
- Read Path
- Journaling
- Write Path
- Working Set
- Capped Collection
- Oplog collection
- TTL Index
- GridFS
Module 3: CRUD Operations
- MongoDB Data Types
- Inserting, Update, Deleting the documents
- Querying the documents
- Bulk insert operation
- Updating multiple document
- Limiting documents
- Filtering documents
Module 4: Schema Design and Data modeling
- Dynamic Schema
- What is Data modeling?
- RDBMS and MongoDB Data modeling difference
- Embedding Document
- Reference Document
Module 5: Indexes
- Index concepts in MongoDB
- Types of indexes
- Indexes and its use cases
- Creating Indexes
- Managing Indexes
- Index strategies
Module 6: Database Administration in MongoDB
- Database status
- Troubleshooting issues
- Current Operations
- Rotating log files
- Users and Roles
- Copy and Clone database
- DB and Collection Stats
- Explain plan
- Profiling
- Changing configuration files
- Upgrading the database
Module 7: MongoDB: Backup and Security
- Concept of backups
- mongoexport/mongoimport
- mongodump/mongorestore
- Oplog backups
- LVM Backups
- Backups using MMS/Ops Manager
- Purpose of security
- Authentication and authorization
- Role based access control
Module 8: Replication in MongoDB
- Concept of replication
- ReplicaSet member roles
- Voting and Electing primary
- Role of Oplog in replication
- Read and Write Concern
- Arbiter,Hidden and Delayed replica node
- Priority settings
- Replicaset nodes health check
- Concept of resyncing the nodes
- Rollbacks during failover
- Keyfile authentication
Module 9: MongoDB Scalability
- Concept of Scalability
- Sharding concept
- Shardkey and Chunks
- Choosing shardkey
- Sharding components
- Types of Sharding
- Balanced data distribution
- Sharded and Non-sharded collection
- Sharded Replicaset
- Tag aware sharding
Module 10: MongoDB Monitoring and Other Tools
- MMS Manager
- Ops Manager
- Mongo utility commands
- Mongo developer tools
- MongoDB Atlas
- MongoDB client drivers
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 the most effective MongoDB online training Institute. it will store complicated structures easily, fetch the info more accurately. Relative databases have rigid schemes that limit flexibility with the data structure. MongoDB works with wealthy JSON Documents, supports a robust query language, Supports aggregations and different trendy use-cases similar to geo-based search, graph search, and text search. It stores knowledge in document format to alter any range of records, add or delete existing fields within the table. There aren't any tables in MongoDB. as a result MongoDB doesn’t have a strictly defined, consistent schema it's a document store database. the two situations that it addresses specifically are indexes that don’t work into memory and write-heavy data.
. the globe is on the brink of an information overload, and large databases are required to store and manipulate this information.
the most effective MongoDB online training Institute. it will store complicated structures easily, fetch the info more accurately. Relative databases have rigid schemes that limit flexibility with the data structure. MongoDB works with wealthy JSON Documents, supports a robust query language, Supports aggregations and different trendy use-cases similar to geo-based search, graph search, and text search. It stores knowledge in document format to alter any range of records, add or delete existing fields within the table. There aren't any tables in MongoDB. as a result MongoDB doesn’t have a strictly defined, consistent schema it's a document store database. the two situations that it addresses specifically are indexes that don’t work into memory and write-heavy data.
. the globe is on the brink of an information overload, and large databases are required to store and manipulate this information.