SOC Analyst Training by Experts
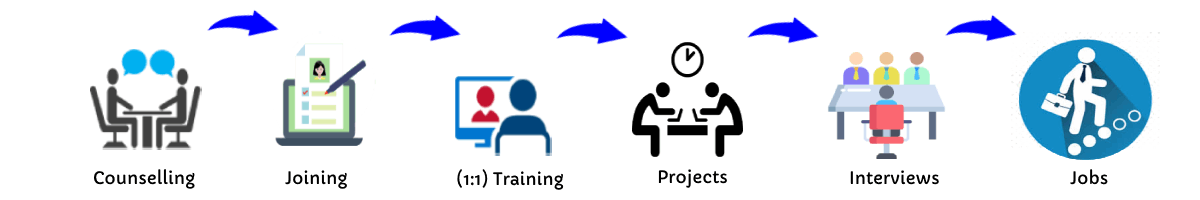
Our Training Process
SOC Analyst - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
Introduction to Cybersecurity
- Basics of cybersecurity
- Common cyber threats and attack vectors
Networking Fundamentals:
- Understanding TCP/IP
- Network protocols
- Firewalls, routers, and switches
Operating Systems
- In-depth knowledge of Windows, Linux, and possibly macOS
- File systems and permissions
Security Technologies
- Antivirus and anti-malware solutions
- Intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS)
- Security information and event management (SIEM) systems
Incident Response
- Incident detection and analysis
- Incident classification and escalation
- Incident documentation and reporting
Threat Intelligence:
- Understanding threat intelligence
- Integrating threat intelligence into daily operations
Security Monitoring:
- Log analysis
- Network traffic analysis
- Endpoint security monitoring
Vulnerability Management
'- Identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities
- Patch management
Security Policies and Compliance
- Understanding security policies and procedures
- Compliance standards and regulations
Hands-on Labs and Simulations
- Practical exercises & simulations for real scenarios
- Use of cybersecurity tools in a controlled environment
Soft Skills
- Communication and collaboration
- Analytical thinking and problem-solving
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 Use security information and event management (SIEM) tools to analyze logs and detect anomalous activities. Vulnerability Assessment:Conduct regular vulnerability assessments to identify weaknesses in the organization's systems and networks. Here are some common tasks and roles performed by cybersecurity analysts:Monitoring Security Infrastructure:Continuously monitor security alerts and events to identify potential security incidents. Develop and implement incident response plans to minimize damage and prevent future incidents. Industry-recognized certifications, such as CompTIA Security+, Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), or Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), may also be part of the training or pursued separately in Ontario . Industry-recognized certifications, such as CompTIA Security+, Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), or Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), may also be part of the training or pursued separately. Stay updated on changes in cybersecurity laws and regulations. . Prioritize and address vulnerabilities to reduce the risk of exploitation. Security Policies and Compliance:Develop and enforce security policies and procedures to ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards.
Use security information and event management (SIEM) tools to analyze logs and detect anomalous activities. Vulnerability Assessment:Conduct regular vulnerability assessments to identify weaknesses in the organization's systems and networks. Here are some common tasks and roles performed by cybersecurity analysts:Monitoring Security Infrastructure:Continuously monitor security alerts and events to identify potential security incidents. Develop and implement incident response plans to minimize damage and prevent future incidents. Industry-recognized certifications, such as CompTIA Security+, Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), or Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), may also be part of the training or pursued separately in Ontario . Industry-recognized certifications, such as CompTIA Security+, Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), or Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), may also be part of the training or pursued separately. Stay updated on changes in cybersecurity laws and regulations. . Prioritize and address vulnerabilities to reduce the risk of exploitation. Security Policies and Compliance:Develop and enforce security policies and procedures to ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards.