IoT (Internet of Things) Training by Experts
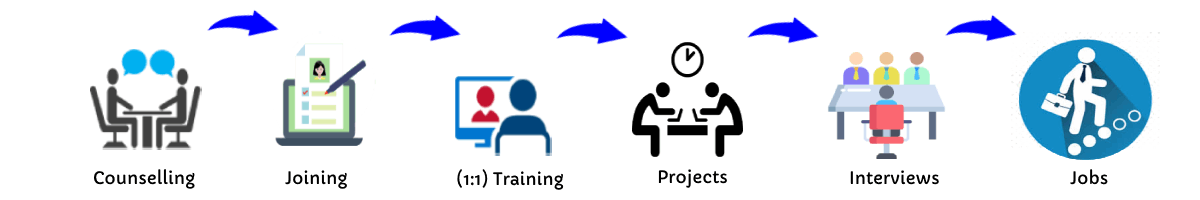
Our Training Process
IoT (Internet of Things) - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
Module 1 - Introduction
- Concepts & Definitions
- Myth with IoT
- Business with IoT
- Carrier in IoT
- IoT Applications
- IoT system overview
- Node, Gateway, Clouds
- Why IoT is essential
- Machine learning
- Artificial Intelligence
Module 2 - IoT Architecture
- IoT Network Architecture
- IoT Device Architecture
- IoT Device Architecture
- Publish-Subscribe architecture
Module 3 - IoT Device Design
- Sensors
- Classification & selection criteria based on the nature ,frequency and amplitude of the signal
- Embedded Development Boards – Arduino, Raspberry Pi, Intel Galileo, ESP8266
Module 4 - IoT Communication Protocols
- Wired Communication Protocols
- Wireless Communication Protocols
- Application Protocols – MQTT, CoAP, HTTP, AMQP
- Transport layer protocols – TCP vs UDP
- IP- IPv4 vs IPv6
Module 5 - Cloud
- Concept & Architecture of Cloud
- Public cloud vs Private cloud
- Different Services in cloud (IAAS / PAAS / SAAS)
- Importance of Cloud Computing in IOT
- Leveraging different Cloud platforms.
Module 6 - Designing The IoT Product
- Interfacing peripherals & Programming GPIOs - Input/output peripherals, Sensor modules
- Design Considerations – Cost, Performance & Power Consumption tradeoffs
Module 7 - Programming
- Embedded C
- Python
- Arduino
Module 8 - Hands-On Using Raspberry Pi Board
- Setting up board
- Booting up Raspberry Pi
- Running python on Raspberry Pi, GPIO programming
- Interfacing sensors and LED (Input and output devices)
- Making a few projects
- Sending data to cloud 2 using Raspberry Pi board
- Sending data to cloud 3 using Raspberry Pi board
- Making raspberry Pi web server
- Making raspberry PI TCP client and server
- Making raspberry Pi UDP client and server
Module 9 - Use Cases
- A cloud-based temperature monitoring system using Arduino and Node MCU
- Esp8266 WIFI controlled Home automation
- Obstacle detection using IR sensor and Arduino
- Remote controlling with Node MCU
- Temperature monitoring using a Raspberry Pi as local server
- Raspberry Pi controlling Esp8266 using MQTT
- weather monitoring system using Raspberry Pi and Microsoft Azure cloud
Module 10 - Closer
- Existing Product in Market
- Barrier in IoT
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 We will remotely monitor our homes and businesses to keep them safe. The expansion of the Internet of Things has aided an increase in the number of deployments in buildings centered on remote monitoring. The advantages of IoT for business depend on how it is implemented; agility and efficiency are frequently top priorities. The Internet of Things (IoT) is a coinage for a network of physical objects linked by sensors, software, and knowledge. Nestsoft will provide the best IoT training on-site with the assistance of field specialists. Maybe you built a smart air conditioner or lighting system with weather-based automation settings. The goal of automation is frequently efficiency, but it's easier said than done if you're acting on instinct or assumptions. They will also examine the costs, efficiencies, and, consequently, the carbon footprint of various resources to make better decisions in their manufacturing operations. The Internet of Things (IoT) is made up of physical devices such as automobiles, home appliances (furniture has joined the party), building materials, and other items that are linked together to collect and exchange data via sensors, software, actuators, microchips, electronics, and other components embedded in them to ensure network connectivity (internet, Bluetooth, etc). Using the power and reach of the internet, the Internet of Things (IoT) has connected a wide range of devices, gadgets, appliances, and infrastructures.
We will remotely monitor our homes and businesses to keep them safe. The expansion of the Internet of Things has aided an increase in the number of deployments in buildings centered on remote monitoring. The advantages of IoT for business depend on how it is implemented; agility and efficiency are frequently top priorities. The Internet of Things (IoT) is a coinage for a network of physical objects linked by sensors, software, and knowledge. Nestsoft will provide the best IoT training on-site with the assistance of field specialists. Maybe you built a smart air conditioner or lighting system with weather-based automation settings. The goal of automation is frequently efficiency, but it's easier said than done if you're acting on instinct or assumptions. They will also examine the costs, efficiencies, and, consequently, the carbon footprint of various resources to make better decisions in their manufacturing operations. The Internet of Things (IoT) is made up of physical devices such as automobiles, home appliances (furniture has joined the party), building materials, and other items that are linked together to collect and exchange data via sensors, software, actuators, microchips, electronics, and other components embedded in them to ensure network connectivity (internet, Bluetooth, etc). Using the power and reach of the internet, the Internet of Things (IoT) has connected a wide range of devices, gadgets, appliances, and infrastructures.