Red Hat Training by Experts
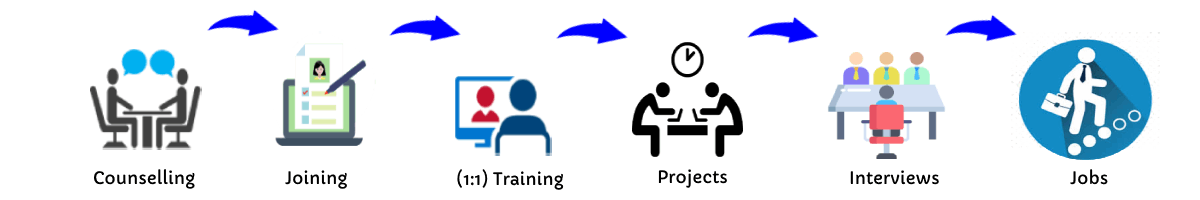
Our Training Process
Red Hat - Syllabus, Fees & Duration
MODULE 1
- Basic system configuration
- Getting started
- The basic configuration of the environment
- Configuring and inspecting network access
- The basics of registering the system and managing subscription
- Installing software
- Making system services start at boot time enhancing system security with a firewall, SELinux, and SSH loggings
- The basics of managing the user account
- Dumpling the crashed kernel using the KDUMP mechanism
- Performing system reuse and creating g backup with rear
- Using the log files to troubleshoot problems
- Accessing red hat support
MODULE 2
- System locale and keyboard configuration
- Setting the system locale
- Changing the keyboard layout
- Additional resources
MODULE 3
- Configuring the date and time
- Using the time DATECTL command
- Using the date command
- Using the hwclock command
MODULE 4
- Managing users and groups
- Introduction to users and groups
- Using command-line tools
MODULE 5
- Access control lists
- Mounting file systems
- NFS
- Setting access ACLS
- Setting default ACLs
- Retrieving ACLS
- Archiving file systems with ACLS
- Compatibility with older systems
- ACL references
MODULE 6
- Gaining privileges
- Configuring administrative access using the SU utility
- Configuring administrative access using the SUDO utility
MODULE 7
- Registering the system and managing subscriptions
- Registering the system and attaching subscriptions
- Managing software repositories
- Removing subscriptions
MODULE 8
- Accessing support using the red hat support tool
- Installing the red hat support tool
- Registering the red hat support tool using the command line
- Using the red hat support tool in interactive shell mode
- Configuring the red hat support tool
- Opening and updating support cases using interactive mode
- Viewing support cases on the command line
MODULE 9
- Yum
- Checking for and updating packages
- Working with packages
- Working with package groups
- Working with transaction history
- Configuring yum and yum repositories
- Yum plug-ins
- Automatically refreshing package database and downloading updates with yum-cron
MODULE 10
- Managing server with system
- Introduction to systems
- Managing system services
- Working with systems targets
- Shutting down, suspending, and hibernating the system
- Controlling system on a remote machine
- Creating and modifying system unit files
- Additional considerations while managing services
MODULE 11
- Configuring a system for accessibility
- Configuring the bratty service
- Switch on always show universal access menu
- Enabling the festival speech synthesis system
MODULE 12
- Open SSH
- The SSH protocol
- Configuring Open SSH
- Open SSH clients
- More than a secure shell
MODULE 13
- Tiger VNC
- VNC server
- Sharing an existing desktop
- VNC viewer
MODULE 14
- Web servers
- The Apache HTTP server
MODULE 15
- Mail servers
- Email protocols
- Email program classifications
- Mail transport agents
- Mail delivery agents
- Mail user agents
- Configuring mail server with ant spam and antivirus
MODULE 16
- Files and print servers
- Samba
- Ftp
- Print settings
MODULE 17
- Database servers
- Maria dB
MODULE 18
- Configuring NTP Using the chrony Suite
- Introduction to the chrony suite
- Understanding chronic and its configuration
- Using chrony
- Setting up chrony for different environments
- Using chronic
- Chrony with hw time stamping
MODULE 19
- Configuring NTP Using NTPD
- Introduction to NTP
- NTP strata
- Understanding NTP
- Understanding the drift file
- Utc, timezones, and DST
- Authentication options for NTP
- Managing the time on virtual machines
- Understanding leap seconds
- Understanding the NTPD configuration file
- Understanding the NTPD sysconfig file
- Disabling chronic
- Checking if the NTP daemon is installed
- Installing the NTP daemon (NTPD)
- Checking the status of NTP
- Configure the firewall to allow incoming NTP packets
- Configure NTP date servers
- Configure NTP
- Configuring the hardware clock update
- Configuring clock sources
MODULE 20
- Configuring PTP using ptp4l
- Introduction to PTP
- Using PTP
- Using PTP with multiple interfaces
- Specifying a configuration file
- Using the PTP management client
- Synchronizing the clocks
- Verifying time synchronization
- Serving PTP Time with NTP
- Serving NTP time with PTP
- Synchronize to PTP or NTP time using time master
- Improving accuracy
MODULE 21
- System monitoring tools
- Viewing system processes
- Viewing memory usage
- Viewing block devices and file systems
- Viewing hardware information
- Checking for hardware errors
- Monitoring performance with net-SNMP
MODULE 22
- Open NLMI
- About open NLMI
- Installing open NLMI
- Configuring SSL certificates for open Pegasus
- Using lmishell
- Using open NLMI scripts
MODULE 23
- Viewing and managing log files
- Locating log files
- The basic configuration of rsyslog
- Using the new configuration format
- Working with queues in rsyslog
- Configuring Syslog on a logging server
- Using rsyslog modules
- Interaction of rsyslog and journal
- Structured logging with Syslog
- Debugging rsyslog
- Using the journal
- Managing log files in a graphical environment
MODULE 24
- Automating system tasks
- Scheduling a recurring job using cron
- Scheduling a recurring asynchronous job using anacron
- Scheduling a job to run at a specific time using at
- Scheduling a job to run on system load drop using batch
- Scheduling a job to run on the next boot using a systemd unit file
MODULE 25
- Automatic bug reporting tools
- Introduction to ABRT
- Installing ABRT and starting its services
- Configuring ABRT
- Detecting software problems
- Handling detected problems
MODULE 26
- Working with grub2
- Introduction to grub 2
- Configuring grub 2
- Making temporary changes to a grub 2 menu
- Making persistent changes to a grub 2 menu using the grubby tool
- Customizing the grub 2 configuration file
- Protecting grub 2 with a password
- Reinstalling grub 2
- Upgrading from grub-legacy to grub 2
- Grub 2 over a serial console
- Terminal menu editing during boot
- Unified extensible firmware interface (UEFI) secure boot
MODULE 27
- Relax and recover
- Basic rear usage
- Integrating rear with backup software
MODULE 28
- Choosing a suitable red hat product
MODULE 29
- Red hat customer portal labs relevant to system administration
- Iscsi Helper
- NTP Configuration
- Samba Configuration Helper
- VNC Configurator
- Bridge Configuration
- Network Bonding Helper
- LVM RAID Calculator
- NFS Helper
- Load Balancer Configuration Tool
- Yum Repository Configuration Helper
- File System Layout Calculator
- RHEL Backup and Restore Assistant
- DNS Helper
- AD Integration Helper (Samba FS - winbind)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Upgrade Helper
- Registration Assistant
- Rescue Mode Assistant
- Kernel Oops Analyzer
- Kdump Helper
- SCSI decoder
- Red Hat Memory Analyzer
- Multipath Helper
- Multipath Configuration Visualizer
- Red Hat I/O Usage Visualizer
- Storage / LVM configuration viewer
This syllabus is not final and can be customized as per needs/updates




 IP to non-IP networking, network-manager, network configuration technique, static, network teaming, and VLAN tagging, troubleshooting network device naming, Infiniband, and RDMA networks, DNS servers are among the topics covered. It's simple to schedule maintenance work, and it's also simple to repair, and it's getting stronger every day. RedHat is a rapidly growing company that is thought to assist a large percentage of Fortune 100 organizations. Storage, operating system platforms, middleware, applications, organizational products, and support, training, and consulting services are all provided by Red Hat. When it comes to processing traffic and large transactions, Red Hat performs admirably. Because there is such a high need for red hat-trained personnel, they go hand in hand. We'll teach technical and non-technical roles in software engineering, quality engineering, project management, IT, human resources, and marketing that offer a lot of freedom. Red Hat provides a wide range of services, including storage, operating system platforms, middleware, applications, management products, education, certifications, and quality assurance.
You will be able to configure local storage, manage system security, effectively handle systems, administer a web server, and manage remote storage by the end of the course. Students who want to be system administrators should start with Red Hat training on-site.
IP to non-IP networking, network-manager, network configuration technique, static, network teaming, and VLAN tagging, troubleshooting network device naming, Infiniband, and RDMA networks, DNS servers are among the topics covered. It's simple to schedule maintenance work, and it's also simple to repair, and it's getting stronger every day. RedHat is a rapidly growing company that is thought to assist a large percentage of Fortune 100 organizations. Storage, operating system platforms, middleware, applications, organizational products, and support, training, and consulting services are all provided by Red Hat. When it comes to processing traffic and large transactions, Red Hat performs admirably. Because there is such a high need for red hat-trained personnel, they go hand in hand. We'll teach technical and non-technical roles in software engineering, quality engineering, project management, IT, human resources, and marketing that offer a lot of freedom. Red Hat provides a wide range of services, including storage, operating system platforms, middleware, applications, management products, education, certifications, and quality assurance.
You will be able to configure local storage, manage system security, effectively handle systems, administer a web server, and manage remote storage by the end of the course. Students who want to be system administrators should start with Red Hat training on-site.